The Technology Behind Producing High-Quality sugar cane products from Field to Factory
The Technology Behind Producing High-Quality sugar cane products from Field to Factory
Blog Article
A Deep Dive Into Sugar Cane: Insights on Production, Supplies, and Product Advancement
Sugar cane plays an important role in agriculture, underpinning economies in tropical areas. Its farming involves detailed processes influenced by different ecological aspects. Cultivators encounter significant challenges, consisting of climate modification and market changes. Technologies in product advancement are arising in feedback to developing customer demands. Recognizing these characteristics is necessary for grasping the future of this crucial plant and its influence on worldwide markets. What lies ahead for sugar cane and its myriad applications?
The Relevance of Sugar Cane in Global Farming
Sugar cane offers as a necessary crop in worldwide agriculture, underpinning economies and food systems in many tropical areas. This functional plant is primarily cultivated for its high sucrose material, which is improved into sugar, a standard ingredient in countless food products. Past sweetening, sugar cane is additionally crucial for creating biofuels, especially ethanol, contributing to power sustainability.The financial value of sugar cane includes work, offering source of incomes for countless farmers and workers in handling centers. In several nations, sugar cane growing and handling represent considerable parts of farming GDP, influencing profession equilibriums and regional development.Additionally, sugar cane's versatility to different environments enhances its importance as a plant, making sure constant supply in international markets. Its byproducts, including molasses and bagasse, further expand its utility, making it a vital element in food, energy, and market. In general, sugar cane remains a keystone of farming performance worldwide.
Cultivation Processes: From Planting to Harvest
Cultivating sugar cane entails a series of well-defined procedures that guarantee ideal development and return. The cultivation starts with land preparation, where the dirt is tilled to safeguard optimal aeration and drain. Following this, seed cane, which includes mature stalks, is picked and reduced right into sectors (sugar cane products). These sectors are then planted in furrows, making sure correct spacing to enable for sunlight and nutrient access.Once grown, watering systems are employed to keep ample moisture degrees, as sugar cane grows in moist problems. Weeding and insect monitoring are necessary during the growing duration to decrease competition for resources. Nutrient application, including fertilizers, sustains robust growth. As the plants develop, keeping track of for diseases and pests continues.Harvesting typically occurs 10 to 24 months post-planting, relying on the selection. The walking sticks are reduced short, guaranteeing very little waste, and are swiftly transferred for processing to protect sugar top quality
Geographical Circulation of Sugar Cane Production
The geographic circulation of sugar cane production is greatly formed by specific climate and soil needs. Major producing countries, such as Brazil, India, and China, benefit from tropical and subtropical climates that sustain the crop's growth. Understanding these elements offers insight right into the global landscape of sugar cane cultivation.
Major Making Countries
Although sugar cane is expanded in numerous regions worldwide, specific countries dominate production due to favorable environments and farming techniques. Brazil leads the worldwide market, representing about one-third of complete production, many thanks to its considerable haciendas and progressed growing methods. India adheres to as a substantial producer, profiting from both favorable weather and a big domestic market. China and Thailand also rate amongst the leading producers, with reputable facilities supporting their sugar markets. Various other noteworthy factors consist of the USA, Mexico, and Australia, each leveraging their one-of-a-kind agricultural systems to boost outcome. These countries play a vital role in the sugar cane supply chain, affecting international rates and accessibility
Climate and Dirt Requirements
Perfect environment and soil conditions are essential for successful sugar cane production. Sugar cane grows in tropical and subtropical areas, requiring cozy temperatures in between 20 ° C and 30 ° C (68 ° F to 86 ° F) These plants require abundant sunshine and rains, ideally in between 1,500 to 2,500 millimeters yearly, to guarantee peak growth. The soil should be well-drained, fertile, and abundant in organic matter, with a pH level ideally between 5.5 and 8.5. Sandy loam or clay loam click here for more dirts are especially for sugar cane farming, providing necessary nutrients and water drainage. Geographical distribution is greatly affected by these variables, with significant production locations situated in Brazil, India, and China, where ecological problems straighten with the plant's requirements for development and return.
Challenges Dealt With by Sugar Cane Growers
Sugar cane cultivators encounter significant challenges that impact their livelihoods. Climate adjustment introduces unforeseeable climate patterns, influencing plant return and high quality. Furthermore, market value volatility develops monetary unpredictability, complicating lasting planning for these agricultural producers.
Environment Change Impacts

Exactly how do environment modification influences affect the viability of sugar cane farming? Climbing temperatures and erratic weather condition patterns notably test sugar cane cultivators. Enhanced heat can result in reduced returns, as the plants struggle to thrive in severe problems. Furthermore, altered rains patterns lead to either droughts or too much flooding, both harmful to crop health. Parasites and illness are likely to multiply in warmer climates, further harmful production. Dirt degradation and salinization due to rising sea levels can lessen cultivatable land. These weather changes oblige cultivators to adjust their techniques, commonly calling for financial investment in new modern technologies and durable plant selections. Ultimately, the sustainability of sugar cane cultivation depends upon attending to these environment challenges successfully.

Market Rate Volatility
Market price volatility provides considerable obstacles for sugar cane cultivators, affecting their financial stability and preparation. Changes in market value, driven by elements such as international supply and demand, weather problems, and government plans, create uncertainty for producers. This unpredictability makes it challenging for cultivators to forecast revenues and handle operating costs effectively. Furthermore, when prices go down all of a sudden, many farmers may struggle to cover production costs, bring about potential financial distress. To reduce these dangers, some growers turn to agreements or hedging strategies, yet these remedies might not be accessible to all. Subsequently, market rate volatility continues to be a relentless problem, affecting the general sustainability and earnings of sugar cane farming.
Recognizing the Sugar Cane Supply Chain

Market Patterns Affecting Sugar Cane Costs
The characteristics of sugar cane costs are influenced by a selection of market fads that mirror more comprehensive financial problems and customer habits. International demand for sugar and sugar-related products plays a crucial duty, with raising passion in natural and sustainably sourced products driving rates higher. In addition, variations in oil rates influence the cost of production and transportation, additional influencing market prices. Climate patterns are one more significant aspect; adverse conditions can bring about minimized yields and raised rates. Profession plans, tolls, and worldwide agreements also shape the market landscape, impacting supply chains and availability. Money exchange rates can complicate global trade, impacting rates for both exporters and importers. Ultimately, changes in consumer choices toward healthier options may change need patterns, producing a causal sequence on sugar cane prices. Comprehending these interconnected patterns is important for stakeholders in the sugar sector.
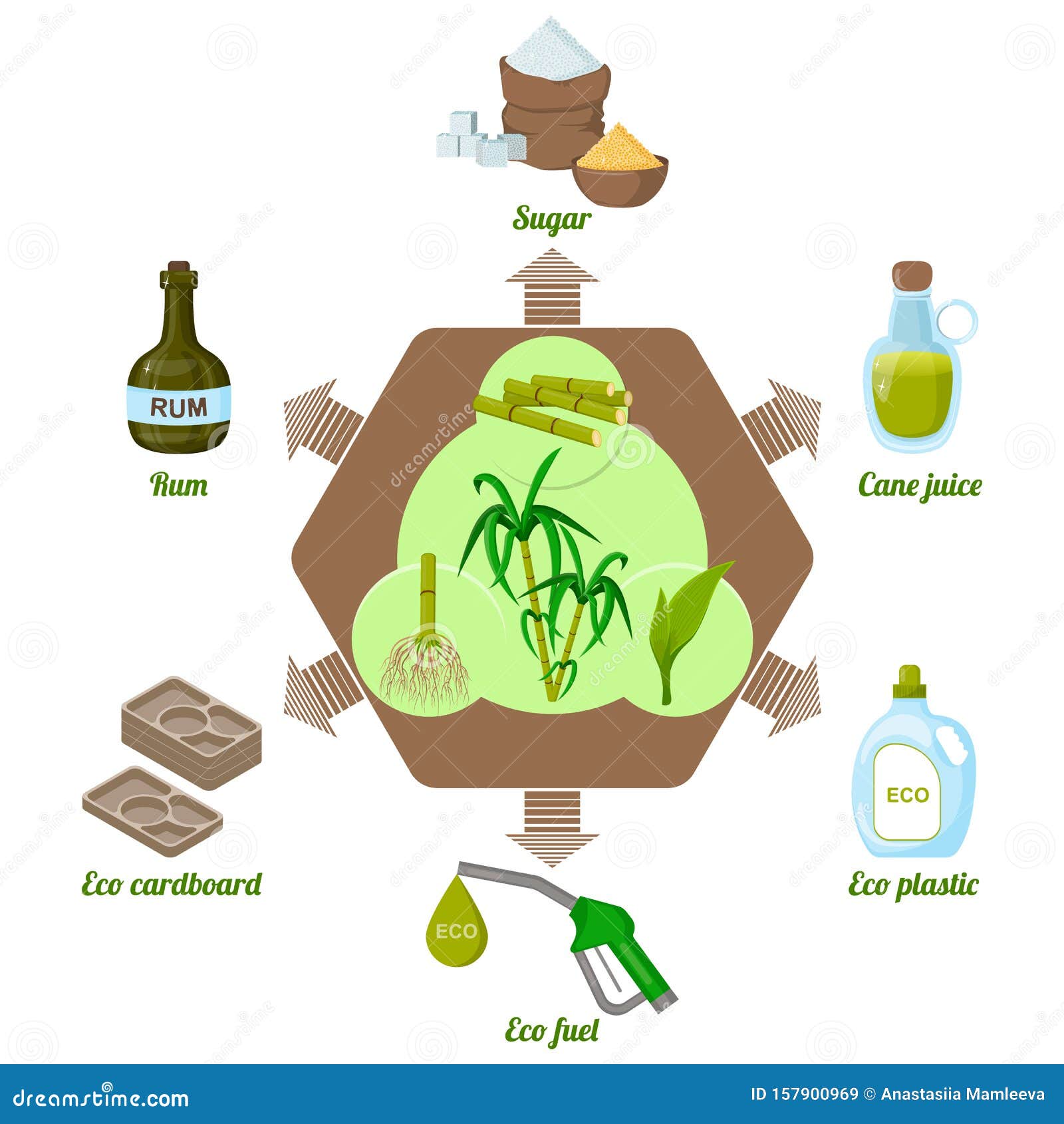
Innovations in Sugar Cane Item Growth
Many advancements in sugar cane product development are improving the industry and broadening its applications. Scientists are checking out different uses past traditional sugar, including biofuels, eco-friendly plastics, and health and wellness supplements. Breakthroughs in enzymatic handling strategies have improved the removal of important substances such as antioxidants and vitamins from sugar cane, promoting its usage in useful foods.Additionally, the development of genetically changed sugar cane varieties intends to boost return and resistance to insects, while likewise boosting the nutritional profile of the crop. Innovations in fermentation processes have actually caused the production of top notch alcohols derived from sugar cane, appealing to a growing market for craft spirits.Moreover, lasting methods in growing and handling are acquiring traction, with a focus on reducing ecological impacts. These innovations not only develop new market chances but likewise cultivate an even more lasting strategy more info here to sugar cane production, straightening with global trends towards environment-friendly items.
Often Asked Concerns
What Are the Ecological Influences of Sugar Cane Farming?
The ecological influences of sugar cane farming consist of logging, loss of biodiversity, water air pollution from fertilizers and pesticides, soil degradation, and greenhouse gas emissions, every one of which considerably add to ecological inequalities and climate adjustment.
How Does Sugar Cane Farming Affect Resident Economies?
Sugar cane growing significantly influences neighborhood economic situations by developing work, promoting agricultural sectors, and generating revenue for farmers. It can likewise lead to economic dependence and changes based on market demands and environmental conditions.
What Are the Key Pests and Diseases Affecting Sugar Cane?
The primary insects affecting sugar cane consist of the sugarcane borer and aphids. Illness such as red rot and smut substantially effect return. Farmers must execute integrated insect administration techniques to minimize these risks efficiently.
Just How Is Sugar Cane Processed Into Different Products?
Sugar cane processing involves squashing the stalks to extract juice, followed by explanation, evaporation, and formation. This process yields raw sugar, molasses, and ethanol, each serving distinctive objectives in various industries, from food to energy.
What Are the Nutritional Aspects of Sugar Cane?
The dietary elements of sugar cane consist of essential vitamins and minerals, specifically B vitamins, calcium, and iron. It likewise has fiber, though mainly made up of sucrose, which supplies power yet lacks significant nutrients.
Report this page